
At MatterHackers, we take pride in offering the largest selection of 3D printing filament available. From our affordable MH Build Series filament to our professional-grade PRO Series filament, you can find any material, like PLA, ABS, NylonX, PETG, TPU, TPE, Flexibles, Polycarbonate, and more! Along with our industry-proven brand of filament, we also carry other top-notch materials from Bambu Lab, Polymaker, Protopasta, and more.
- PLA, ABS, PETG, ASA, Nylon & More
- Dual-Color, Support, & Metal Filaments
- MH Build, PRO Series, & Specialty Brands
3D Printer Filament Collections
All 3D Printer Filament
About 3D Printer Filament
What is 3D Printing Filament?
3D printing filament is a type of material used in 3D printing, a process that creates three-dimensional objects layer by layer from a digital file. Filament is the "ink" for 3D printers, specifically for Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) or Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) printers. These printers work by melting the filament and extruding it through a heated nozzle to build objects layer by layer.
Types of 3D Printing Filaments:
- PLA (Polylactic Acid): PLA is one of the most popular and easy-to-use filaments. It is biodegradable, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, and produces minimal odor when printed.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): ABS is known for its strength and durability. It is less brittle than PLA and is often used for functional parts and prototypes. However, it requires a heated bed and proper ventilation due to the fumes it emits.
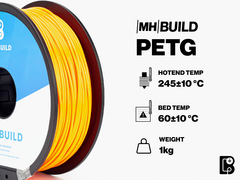
- PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol): PETG combines the ease of use of PLA with the strength and durability of ABS. It is resistant to impact and moisture, making it suitable for a variety of applications.
- TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane): TPU is a flexible filament that is perfect for creating rubber-like parts. It is durable and resistant to abrasion and impact.
- Nylon: Nylon is a strong, flexible, and durable filament. It is often used for mechanical parts and tools due to its high strength and wear resistance.
Choosing the Right Filament:
When selecting a 3D printing filament, consider the following factors:
- Material Properties: Depending on your project, you may need a filament that is strong, flexible, or heat-resistant.
- Printer Compatibility: Ensure that your 3D printer supports the filament type you intend to use.
- Printing Conditions: Some filaments require specific conditions, such as a heated bed or an enclosed printing environment.
- End-Use Application: Choose a filament that meets the requirements of your final product, whether it’s for prototyping, functional parts, or artistic creations.
|
Filament |
Common Transition Temps |
Common Bed Temps |
Printing Surface |
|
PLA |
205±15 °C |
40±15 °C |
Glass |
|
ABS |
230±10 °C |
90±10 °C |
Glass with ABS slurry or kapton tape |
|
PETG |
245±10 °C |
60±10 °C |
Blue painters tape or bed adhesive |
|
Nylon |
255±15 °C |
70±10 °C |
Garolite |
|
ASA |
250±10 °C |
90±10 °C |
Hairspray, bed adhesive |
|
Polypropylene |
250±15 °C |
110±10 °C |
Packing tape or polypropylene |
|
TPU/TPE |
230±10 °C |
50±15 °C |
Glass, painters tape |
|
PCTPE |
235±10 °C |
70±10 °C |
Glass with kapton tape or hairspray |
|
Polycarbonate |
290±20 °C |
130±15 °C |
Gluestick/hairspray |
|
PVA Support |
180±20 °C |
45±10 °C |
LayerLock PEI |
|
Breakaway Support |
210±10 °C |
50±5 °C |
LayerLock PEI |
|
HIPS Support |
230±10 °C |
50±10 °C |
Glass with kapton tape or hairspray |